What Is a Supermoon and When Is the Next One?
When the Full Moon or New Moon occurs near the Moon’s closest approach to Earth, its perigee, it is often called a Supermoon.

A Super Full Moon can be an awesome sight, especially at moonrise.
©iStockphoto.com/4FR
When’s the Next Supermoon?
The next Super Full Moon is on December 24, 2026 (UTC).
Super Moons can also occur in the opposite part of the lunar month, at New Moon.
The next Super New Moon is on May 16, 2026 (UTC).
Super New Moons, like any other New Moon, are usually not visible from Earth, but the dark night skies provide great opportunities for some night sky watching.
Super Full and New Moon
When a Full Moon takes place when the Moon is near its closest approach to Earth, it is called a Super Full Moon. When there is a New Moon around the closest point to Earth, it is known as a Super New Moon.
A Micromoon, on the other hand, is when a Full or a New Moon is near its farthest point from Earth, around apogee. It’s also known as a Minimoon, Mini Full Moon, or a Mini New Moon.
How can Full Moon be in the daytime?
The Moon: Our natural satellite
Perigee and Apogee
A New Moon at perigee is also often referred to as a Supermoon. However, this event usually garners less attention because a New Moon is invisible from Earth.
The Moon’s orbit around Earth is not a perfect circle, but elliptical, with one side closer to Earth than the other. As a result, the distance between the Moon and Earth varies throughout the month and the year. On average, the distance is about 382,900 kilometers (238,000 miles).
The point on the Moon’s orbit closest to Earth is called the perigee and the point farthest away is the apogee.
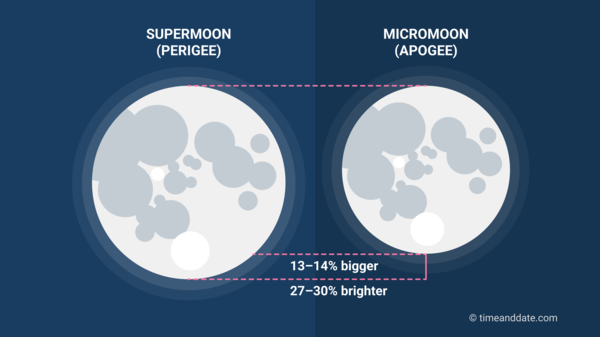

A Supermoon looks larger than a Micromoon.
Not an Official Name
Supermoon is not an official astronomical term. It was first coined by an astrologer, Richard Nolle, in 1979. He defined it as ‘a New or a Full Moon that occurs when the Moon is at or near (within 90% of) its closest approach to Earth in its orbit’. It is not clear why he chose the 90% cut off in his definition.
Supermoon Definition
There are no official rules as to how close or far the Moon must be to qualify as a Supermoon or a Micro Moon. Different outlets use different definitions. Due to this, a Full Moon classified as a Supermoon by one source may not qualify as a Super Full Moon by another.
The following definitions are used at mungfali.galihkartiwa07.workers.dev:
- Supermoon: A Full or New Moon that occurs when the center of the Moon is less than 360,000 kilometers (ca. 223,694 miles) from the center of Earth.
- Micromoon : A Full Moon or New Moon that takes place when the center of the Moon is farther than 405,000 kilometers (ca. 251,655 miles) from the center of Earth.
A Super Full Moon’s angular size is 12.5%–14.1% bigger than a Micro Full Moon, and 5.9%–6.9% bigger than an average Full Moon (in years 1550–2650).
Astronomical terms & definitions
Technical Name: Perigee-syzygy
The technical term for a Supermoon is perigee-syzygy of the Earth-Moon-Sun system. In astronomy, the term syzygy refers to the straight-line configuration of three celestial bodies. Another name is perigee Full Moon.
When the Moon is close to the lunar nodes of its path during a syzygy, it causes a total solar eclipse or a total lunar eclipse

The Moon near the horizon looks larger than when the Moon is higher in the sky, a phenomenon known as the Moon illusion.
©iStockphoto.com/Jason Woodcock
Looks Bigger and Brighter
Because it’s so close to Earth, a Super Full Moon also looks about 30% brighter than a Micro Full Moon and about 16% brighter than an average Full Moon.
The Supermoon on November 14, 2016, was the closest since January 26, 1948. The next time a Full Moon will come even closer to Earth is on November 25, 2034 (dates based on UTC time).
Moon Illusion: Best at Moonrise and Moonset
The best time to enjoy a Super Full Moon, or any other Full Moon, is just after moonrise, when the Moon is close to the horizon. Just before moonset is also a good time.
When the Full Moon is low, it looks bigger and brighter than when it’s higher up in the sky. This is called the Moon illusion, and actually makes more of a difference to what it looks like than the real boost you get from it being a bit closer to Earth.
Higher Tides at Supermoon
The greatest difference between high and low tide is around Full Moon and New Moon. During these Moon phases, the gravitational forces of the Moon and the Sun combine to pull the ocean’s water in the same direction. These tides are known as spring tides or king tides.
Supermoons lead to around 5 cm (2 inches) larger variation than regular spring tides, called perigean spring tides.
The tidal range is smallest during the two Quarter Moons, known as neaps or neap tide.
Sleep, crime, and menstruation: how Full Moons affect humans
Natural Disaster Trigger?
Although the Sun and the Moon’s alignment cause a small increase in tectonic activity, the effects of the Supermoon on Earth are minor. Many scientists have conducted studies, and they haven’t found anything significant that can link the Super Moon to natural disasters.
According to NASA, the combination of the Moon being at its closest and at Full Moon, should not affect the internal energy balance of the Earth since there are lunar tides every day.