What Is a Partial Lunar Eclipse?
A partial lunar eclipse happens when the Earth moves between the Sun and the Full Moon, but they are not precisely aligned. Only part of the Moon's visible surface moves into the dark part of the Earth's shadow.

Next Partial Lunar Eclipse: Fri, Aug 28, 2026 … See animation
Next Eclipse: Annular Solar Eclipse – Tue, Feb 17, 2026 … See animation

A partially eclipsed Moon.
©iStockphoto.com/cinoby
What Causes a Partial Lunar Eclipse?
A partial lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth moves between the Sun and Moon but the three celestial bodies do not form a straight line in space. When that happens, a small part of the Moon's surface is covered by the darkest, central part of the Earth's shadow, called the umbra. The rest of the Moon is covered by the outer part of the Earth's shadow called the penumbra.
Why are there different shadows?
Conditions for a Partial Lunar Eclipse
For a partial lunar eclipse to occur, two celestial events must happen at the same time:
- A Full Moon.
- The Sun, Earth, and Moon must be aligned in almost a straight line.
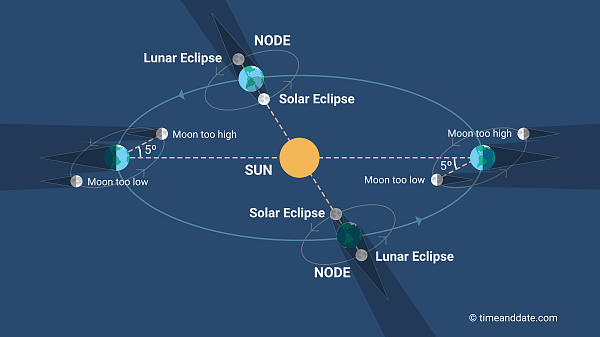

Lunar nodes are the locations where the Moon crosses the Earth's orbital plane.
Not Every Full Moon Night
Partial lunar eclipses do not happen every Full Moon night because of the inclination of the Moon's orbital plane. The Moon's orbital path around the Earth is inclined at an angle of 5° to the Earth's orbital plane (the ecliptic) around the Sun. The points where the two orbital planes meet are called lunar nodes.
Lunar eclipses occur when the Moon is near a node at Full Moon and solar eclipses take place when it is near a node at New Moon.
What is a total lunar eclipse?
Stages of a Partial Lunar Eclipse
- Penumbral eclipse begins: The Earth's penumbra starts covering the Moon's surface.
- Partial eclipse begins: The Earth's umbra starts moving over the Moon.
- Maximum eclipse: The Earth's umbra covers the largest part of the Moon.
- Partial eclipse ends: The Earth's umbra no longer covers the Moon.
- Penumbral eclipse ends: The Earth no longer casts a shadow on the Moon. This marks the end of the eclipse.
The Moon's orientation in the sky depends on the observer's latitude. This means the eclipse will appear to play out in different directions depending on your location.
What happens in a penumbral lunar eclipse?
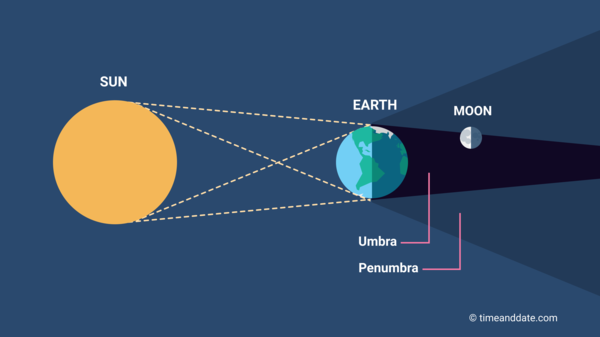
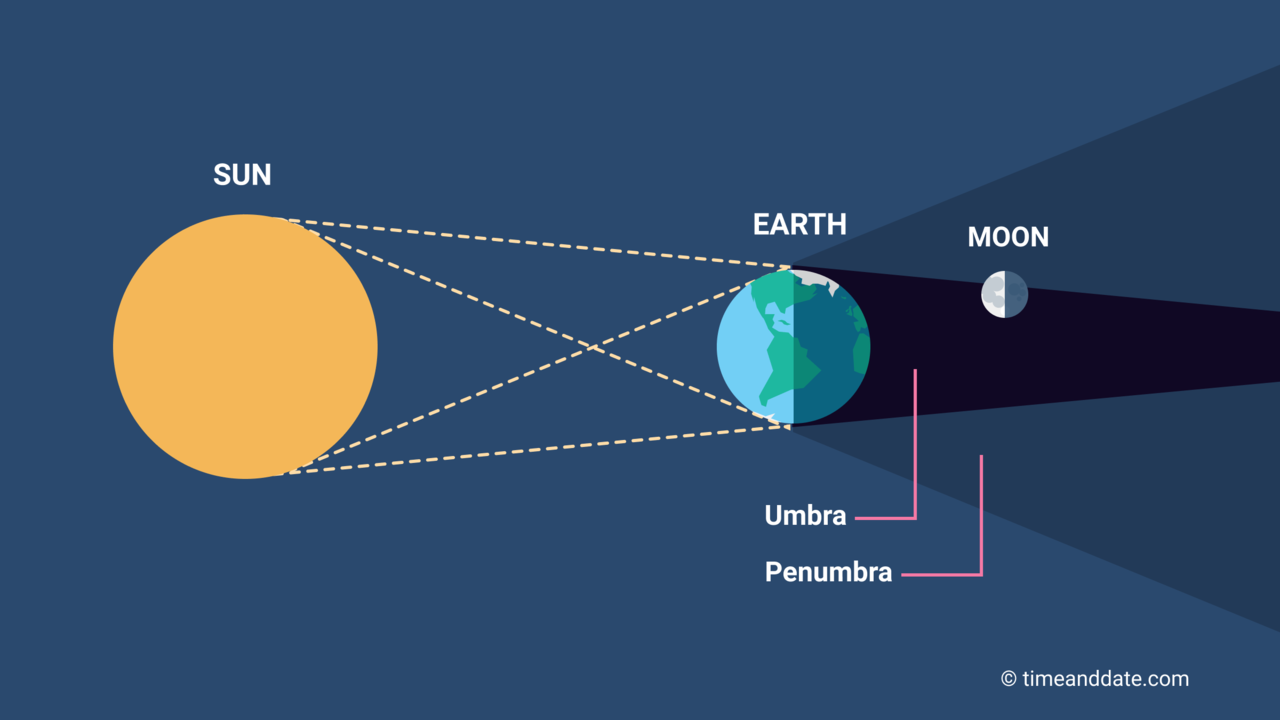
Part of the Moon dips into the Earth's umbra during a partial lunar eclipse.
©mungfali.galihkartiwa07.workers.dev
How to See?
Partial lunar eclipses can be seen across the night-side of the Earth. No special equipment is needed to see a partial lunar eclipse. All you need is the exact date and time for the next eclipse to be seen from where you are, the weather forecast, some warm clothes, and a chair to keep you comfortable while you watch the eclipse unfold.