Daylight Saving 2025 Starts in Canada
Canada begins Daylight Saving Time (DST) on March 9, 2025, but some provinces and territories seek to end seasonal clock changes.
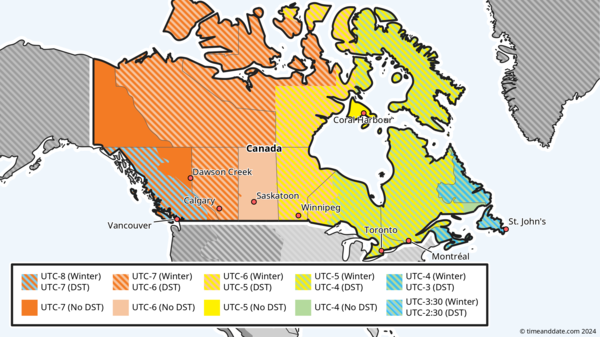

The striped areas will start Daylight Saving Time on March 9, 2025.
©mungfali.galihkartiwa07.workers.dev
Most people living in Canada will set their clocks forward one hour from 02:00 (2 am) to 03:00 (3 am) local time on March 9, 2025.
Standard time, also known as winter time, will resume on Sunday, November 2, 2025.
Most of the United States will also begin DST on the same date.
Longer than in Europe
In 2007, the United States and Canada implemented changes to “spring forward” earlier and “fall back” later. They extended Daylight Saving Time to last 238 days, giving Americans and Canadians more daylight hours in the evening during much of the year. Daylight Saving Time in Europe is 21 or 28 days shorter than in the United States and Canada, depending on the calendar year.
In Europe, DST will end a week before Canada, on October 26, 2025.
DST Change
Clocks will change in almost all areas in Canada, except:
- Yukon (on permanent DST since 2020)
- Some areas in British Columbia
- Most of Saskatchewan
- Southampton Island
- Some locations in Québec east of 63° west longitude (e.g., Blanc-Sablon)
Canada Moves Toward Ending Clock Changes
Several Canadian provinces, including British Columbia (BC), Ontario, and Alberta, have pushed to end Daylight Saving Time (DST), but progress remains slow.
BC introduced a legislation amendment in 2019 to stay on permanent DST but is waiting for Washington, Oregon, and California to take action to maintain alignment.
Ontario passed the Time Amendment Act in 2020 to remain on DST year-round. But they are unlikely to implement it until New York State and Québec formalize their positions, again to ensure alignment on trade and other economic factors.
In 2021, Alberta held a referendum on abolishing the biannual time change. The public vote was a narrow result in favor of retaining the system of adjusting clocks twice a year.
History of DST
Canada implemented DST as far back as 1908, making the small towns of Port Arthur and Fort William (later Thunder Bay) the first documented cases of Daylight Saving Time being adopted in the world.
Other Locations That Change
Also starting DST on March 9, 2025, are Cuba, Bermuda, The Bahamas, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, and Thule Air Base in Greenland.